Environmental Relative Moldiness Index
ERMI tests are generally considered to be accurate, but it’s important to note that they can only test for the presence of mold, not for the amount of mold present. This means that ERMI tests can’t tell you how dangerous the mold in your home is.
How can we best utilize ERMI Scores?
During a mold and moisture inspection an ERMI analysis offers data useful to assist in the assessment of the home by a qualified professional. It is important to point out this testing should be conducted with other sampling types and that the health of a space not be determined based on these results alone. In fact, the EPA has stated that the ERMI has not been validated for routine public use in homes, schools, or other buildings.
If the ERMI score indicates that there may be water damage in the house, further detailed inspection, including additional testing such as bulk, mold swab and/or spore trap testing may reveal a concealed source of water damage and/or mold.
Dust is collected either with a swiffer towelette, bulk sampling, or vacuum dust collection canister.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) developed an index for indoor mold analysis called ERMI (Environmental Relative Moldiness Index). The ERMI test is based on state of the art DNA testing (MSQPCR) to identify molds that are linked to water intrusion and various respiratory diseases such as Asthma, Chronic Sinusitis, and Infant Wheezing. The results obtained from this test give each home a meaningful ERMI score, which can be compared to the 1,100 homes that were studied by the EPA.
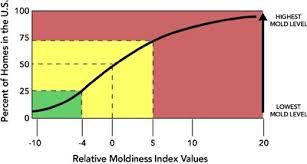
Homes and businesses receiving a high ERMI score are more likely to have unwanted indoor mold growth than those that receive a low ERMI score.
What is an ERMI Score?
The ERMI panel includes 26 mold species known to thrive in water damaged homes and 10 species found in all homes, with or without water damage. Each species and group of species is enumerated from DNA extracted from dust samples, which are taken in both the living and sleeping quarters of the home. Concentrations of each of the 36 molds are used to derive an “ERMI score” that rates the moldiness of each sample against those tested by the US-EPA. These values range from approximately –10 (low moldiness) to 20 (high moldiness), with an average home having a score of 0.
Molds tested for:
Group I (Water Damage Indicators)
Aspergillus flavus
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus niger
Aspergillus ochraceus
Aspergillus penicillioides
Aspergillus restrictus
Aspergillus sclerotiorum
Aspergillus sydowii
Aspergillus unguis
Aspergillus versicolor
Eurotium (A.) amstelodami
Aureobasidium pullulans
Chaetomium globosum
Cladosporium sphaerospermum
Paecilomyces variotii
Penicillium brevicompactum
Penicillium corylophilum
Penicillium crustosum (group2)
Penicillium purpurogenum
Penicillium spinulosum
Penicillium variabile
Scopulariopsis brevicaulis
Scopulariopsis chartarum
Stachybotrys chartarum
Trichoderma viride
Wallemia sebi
Group II (Ubiquitous Fungi)
Acremonium strictum
Alternaria alternata
Aspergillus ustus
Cladosporium cladosporioides I
Cladosporium cladosporioides II
Cladosporium herbarum
Epicoccum nigrum
Penicillium chrysogenum
Rhizopus stolonifer